Cyberpunk 2077, Red Dead Redemption 2, even older titles like the Witcher 3 are all graphics gems. You can enjoy just their graphics for hours on end.
Your joy may be interrupted by an existential question, though:
How much power is this beast actually using?
And you’d be asking the right question. Modern gaming PCs draw a ton of amperage to run these lifelike games and other intensive processes you might be using. Combine that with fancy peripherals, and you’ll find that your PC is making you foot an exorbitant electricity bill.
But even if you’re willing to pay a high electricity bill regularly, you still shouldn’t ignore your PC’s amperage. It has other implications, which we’ll get into in this article.
Read on, as we’ll cover gaming PC amperage in detail so you calculate your computer’s power demands. You can also use the Table of Contents to navigate to whatever interests you most.
A simple formula
You can calculate your amperage by dividing the number of watts your setup draws by the number of volts supplied to you in your area.
For a gaming PC, the wattage will depend on your setup and what you use your PC for. For instance, a multi-monitor setup with an RGB keyboard and mouse and speakers will use more than a basic gaming PC.
Also, running more intensive games or applications will draw more watts than surfing the net.
As for the voltage, it’s determined by your country’s voltage supply and is out of your control. You can find your country’s voltage supply by Googling it (e.g., voltage supply in Germany).
By our estimates, gaming PCs draw an average of 300-600 watts. At 120 volts supplied, that’s between 2.5 and 5 amps.
Why Do You Need to Be Careful With Amperage?
Your computer receives a certain amount of power from your power supply unit (PSU). How much power exactly depends on what PSU you bought. And if your PSU is too weak to handle your PC’s power demands, then there are a few implications.
Some of the most significant implications you can expect are seeing your hardware malfunction or blowing up an electric circuit. But even if you solve any power supply issues and your PC is drawing enormous amounts of power, this will reflect on your electricity bill.
Let’s talk about these implications in a little more detail.
Parts malfunction
By the laws of electronics, if your PC is drawing more power than your power supply is supplying, then the output voltage will suddenly dip to zero and the parts drawing this voltage will stop working due to overload.
Your power supply is designed to detect this overload and shut itself down for a limited time.
However, some PSUs aren’t very intelligent and may go into cycles of turning on and off repeatedly, which will cause the unit to kill itself and possibly kill other devices connected to it.
Blowing up your electric circuit
In some cases, if your PC demands extreme amounts of power or your PSU is inexpensive, the PSU’s capacitors could blow up, which could fry your PSU, motherboard, or any other parts connected to the power supply.
Depending on the quality of your PSU, it might even catch fire. If it’s not contained properly, it can spread to other parts and destroy your entire build. Also, you can expect a dose of burnt plastic smoke in your area.
Be careful because the PSU fire can spread outside your computer build and into your house, too, especially if the PSU’s fans disable themselves. Admittedly, there’s a fraction of a percent that your PSU can cause a structural fire, but why take chances?
Yes, it’s that dangerous. So you should make sure to get a high-quality power supply unit.
Raising your electricity bill
Nowadays, most gaming PCs add a negligible amount to your electricity bill. However, some factors may increase the bill drastically.
Where you live and how much you’re charged per kilowatt-hour (kWh) matters. For instance, the average electricity cost in America is 15 cents per KWh, while in Germany, it’s 37 American cents per kWh.
Your setup, the quality of your PSU, and what you use your PC for will also affect the bill.
Then again, most people won’t have a massive problem with this, but we thought it’s worth mentioning.

What makes up amp usage?
To calculate amperage, you first need to know what an amp is.
For those who don’t, an amp (short for ampere) is an electric current unit. Amperage is calculated by dividing the wattage by the voltage.
But what determines the wattage and voltage, we hear you ask? So that’s what we’ll discuss in this section.
How many watts does a gaming PC use?
Again, your PC’s wattage depends on the parts and your usage.
A common misunderstanding is that your power supply’s wattage capacity determines how many watts your PC uses. But this isn’t true.
If you have a reasonable 400-watt PSU, it doesn’t mean your PC is constantly using 400 watts; it means that your power supply won’t handle more than 400 watts.
For your convenience, here’s a table of the most common gaming PC parts and their wattage. Perhaps this table can help you decide on a power supply unit too.
| Part | Wattage |
| Intel Core i7 | 65-150 W |
| AMD 8-Core CPU | 95-125 W |
| High-End Motherboard | 40-80 W |
| High-End Graphics Card | Up to 20 W when idleUp to 260 W at full load |
| Top-End Graphics Card | Up to 53 W when idleUp to 350 W at full load |
These are the most power-intensive parts. The parts we left out (such as RAM, HDD, SSD, etc.) have a negligible wattage in comparison. For instance, DDR3 RAM uses about 3 watts.
What is your voltage supply?
Finally, you should know the voltage supply in your country. You have no control over the voltage supply, but you can use it to calculate your computer’s amperage.
To find your country’s voltage supply, you can run a quick Google search. But we went ahead and listed the countries where gaming is most popular and their corresponding voltage supply anyway.
| Countries | Voltage Supply |
| Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain | 230 V |
| China, South Korea | 220 V |
| United States, Canada | 120 V |
| Japan | 100 V |
Example Scenario
Suppose your gaming PC draws 600 watts and that you live in the USA, which has a voltage supply of 120. In this case, your computer’s amperage would be 600/120 = ~5 amperes.
Most people won’t go over six amps.
However, if you’re in the minority that has a beefy top-end setup with multiple monitors and RGB peripherals and a fancy 1,000-watt power supply, you’d be clocking in at 8.33 amperes.
How to calculate your computer’s power consumption?
Now that you know your setup’s wattage and your area’s voltage supply, you can divide the wattage by the voltage to get the amperage.
But sometimes it doesn't work as accurately as you'd like it to be.
If you want to be sure about your PC’s power consumption, you can get an accurate wattage using a Kill A Watt meter.
Simple trick: using a Kill A Watt meter
Even with everything mentioned in this article, which is mostly theoretical, your situation may be nuanced. And your electric consumption is most likely not the same as anyone else’s, even if you have the same setup.
The solution? Measure your computer’s wattage yourself!
The best way to do this is to use a Kill A Watt meter, a budget-friendly device that can measure the wattage of anything in your house.
|
Spotlight
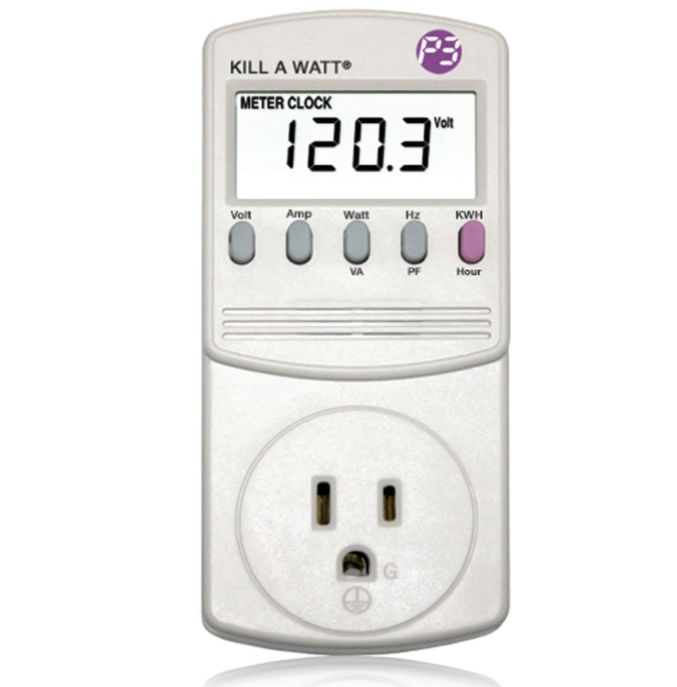 |
P4400 Kill-a-Watt
|
Check Price (Amazon) |
To start, turn your computer off, plug it into your Kill A Watt, then plug the Kill A Watt into the wall.
You could also plug the entire surge protector into your Kill A Watt instead of just your computer so that you can measure the wattage of your entire setup, including your peripherals.
Once everything is plugged, tap the “KWh” button on your Kill A Watt meter, turn your PC on, and use it normally.
You can keep the Kill A Watt plugged in and forget about it, but check it once a day to see how your power consumption is going.
The Bottom Line
That’s about it for our gaming PC amperage guide.
To recap, the amperage is measured by dividing your setup’s wattage by the voltage supply in your area.
Most setups won’t go over 700 watts, and the average voltage supply in the most popular countries for gaming is between 100-230 volts. So we estimate that the average gaming PC amperage is six amps.
You should also be wary of your computer’s power consumption and ensure that your power supply can handle it. Otherwise, you might face implications such as a brownout (power supply safety shutdown), fried parts, or even a fire in some rare cases.
|
Spotlight
 |
P4400 Kill-a-Watt
|
Check Price (Amazon) |
- Big and Tall Gaming Chairs – Ultimate Buyer’s Guide - December 8, 2022
- How Many Fans Do I Need for My Gaming PC - October 6, 2021
- How Many Amps Does a Gaming PC Use: Accurate Explanation - October 5, 2021